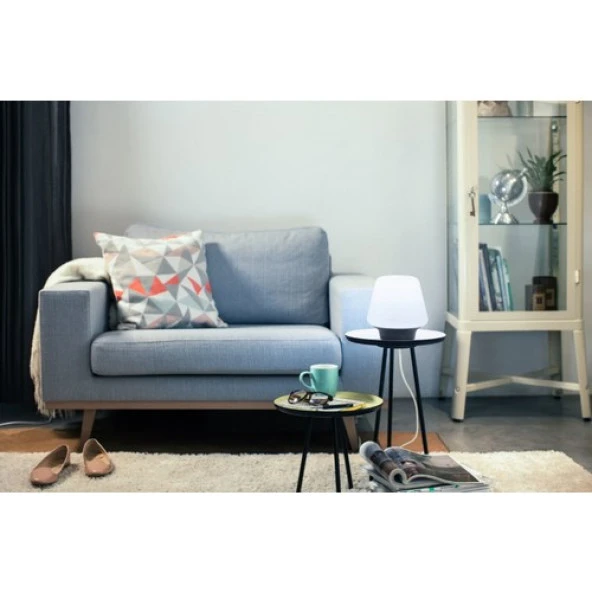
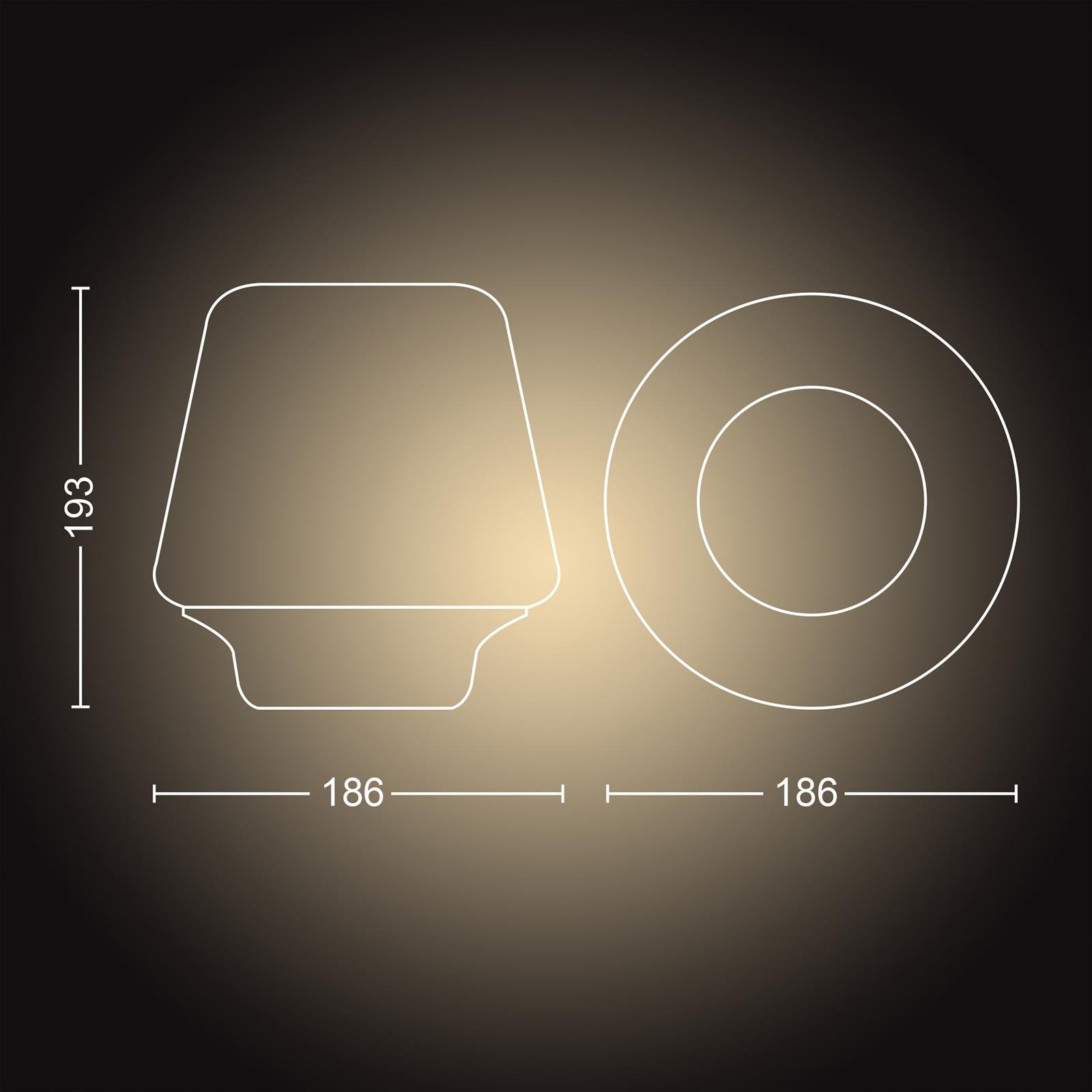
Philips Hue White Amb. LED masa lambası Wellness kısma şalteri dahil, siyah, kısılabilir, tüm beyaz gölgelemeler, uygulama üzerinden kontrol edilebilir, Amazon Alexa (Echo, Echo Dot) ile uyumlu : Amazon.com.tr: Ev ve Yaşam
.jpeg)
Philips Hue - Wellness Hue Masa Lambası - Beyaz Ambiyans - 915005912301 | Aydınlatma Toptan satış | Merkandi arşivi | Merkandi B2B
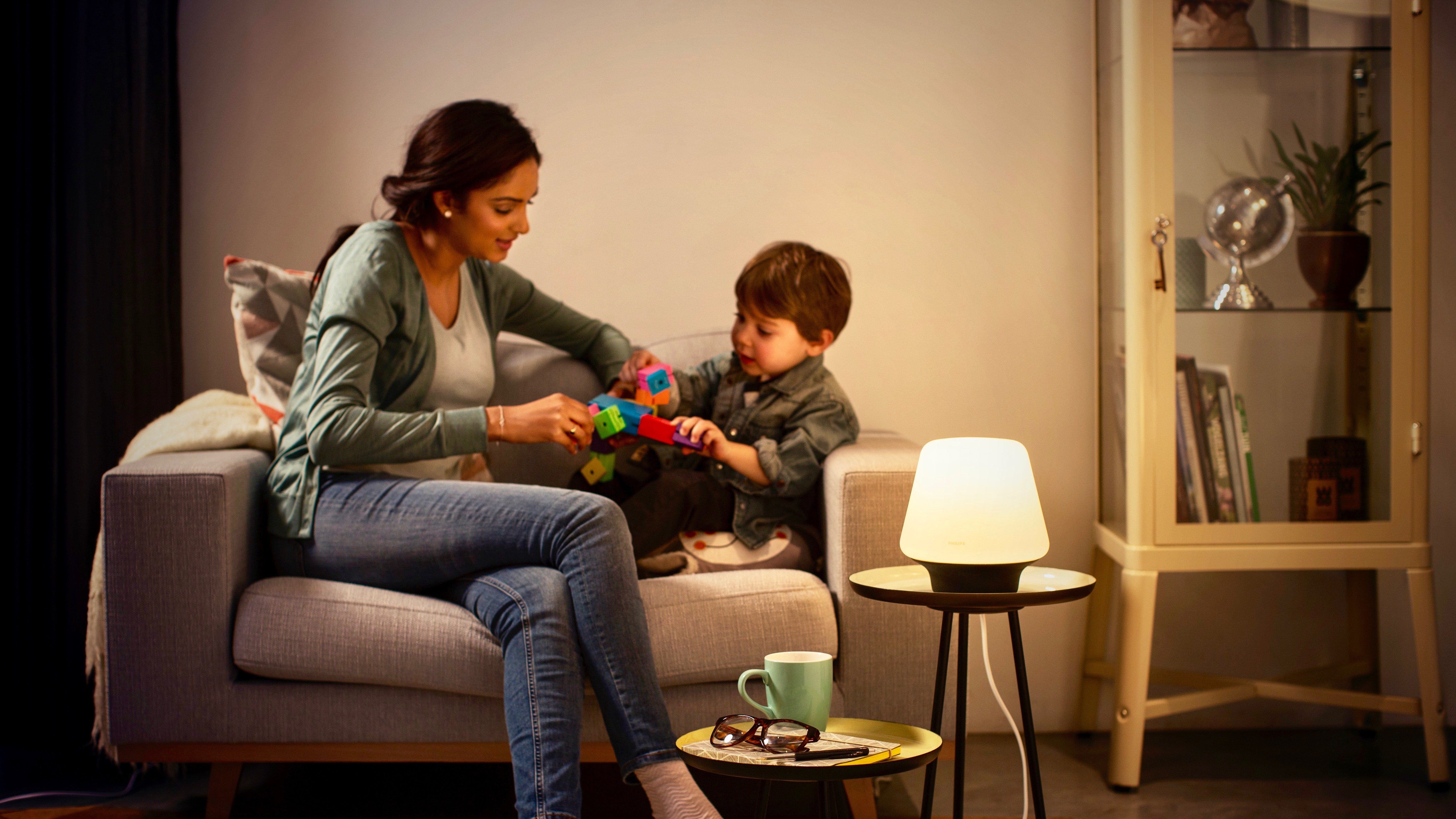

Philips expands HomeKit-compatible Hue White Ambiance line with new table lamps and fixtures - 9to5Mac
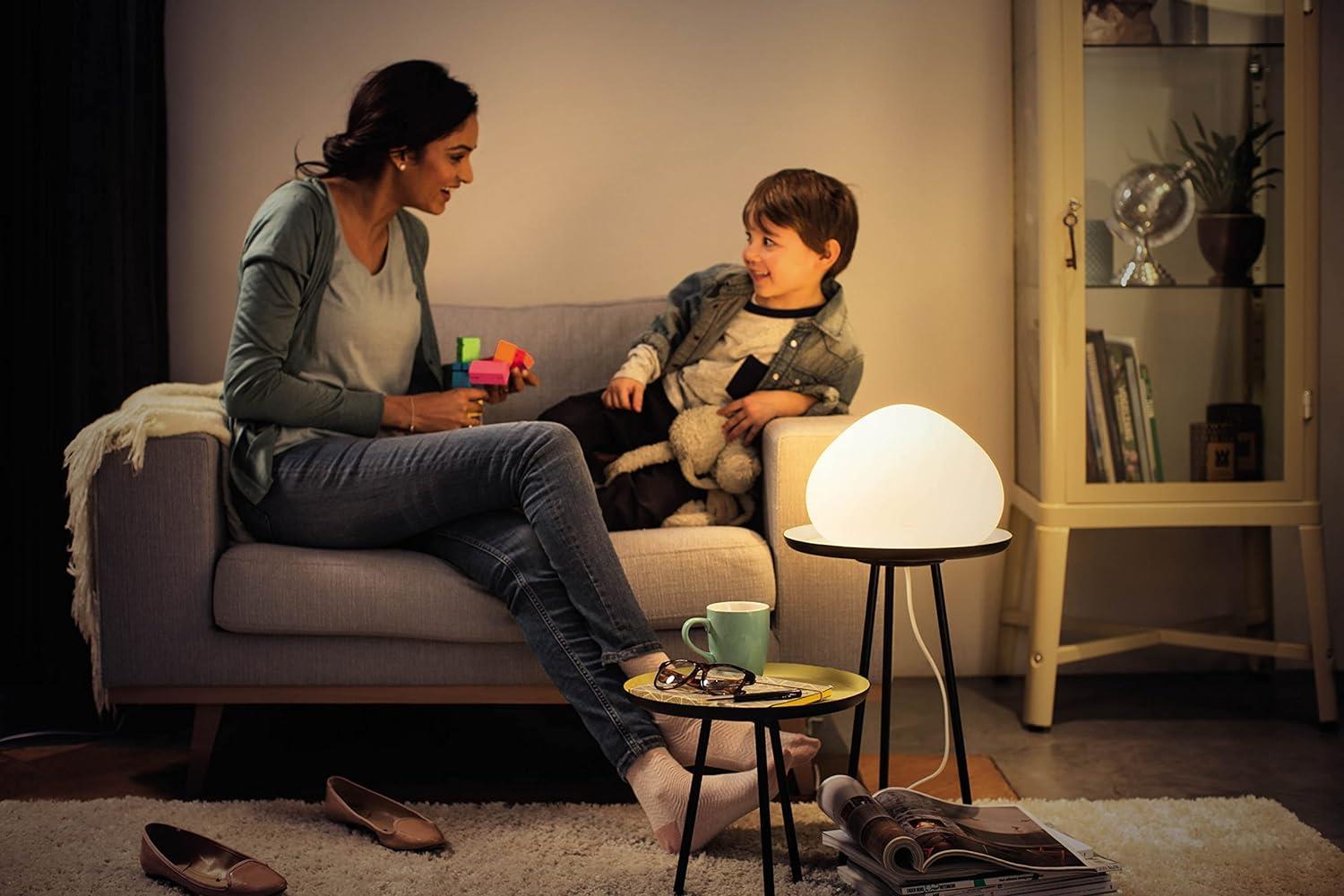
















/cdn1.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/8519341/wellner_and_wellness.png)



