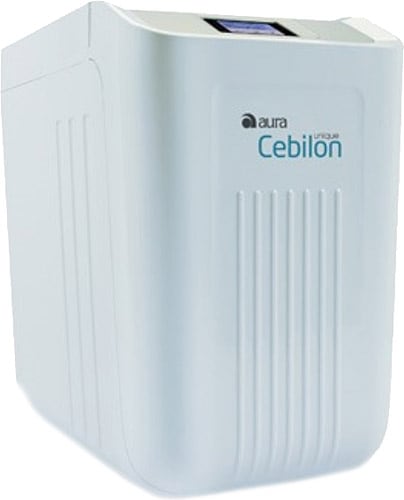
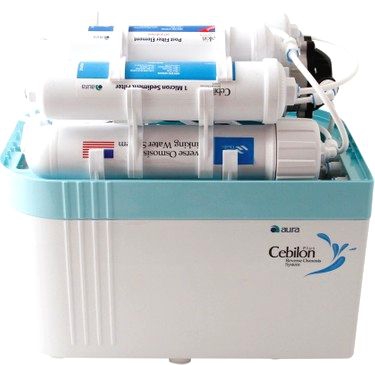
Filtre Dünyası Ihlas Aura Cebilon Su Arıtma Filtresi Takım 5Li Set Çift Karbonlu Fiyatları ve Özellikleri
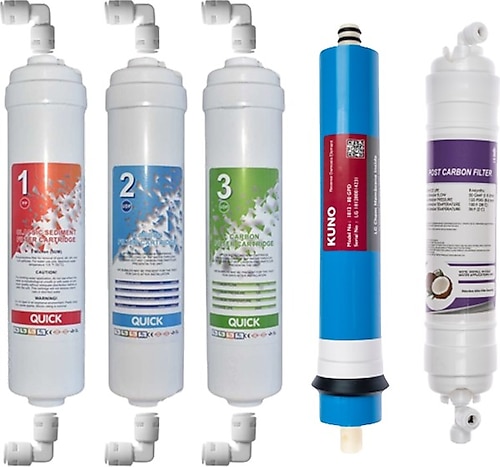

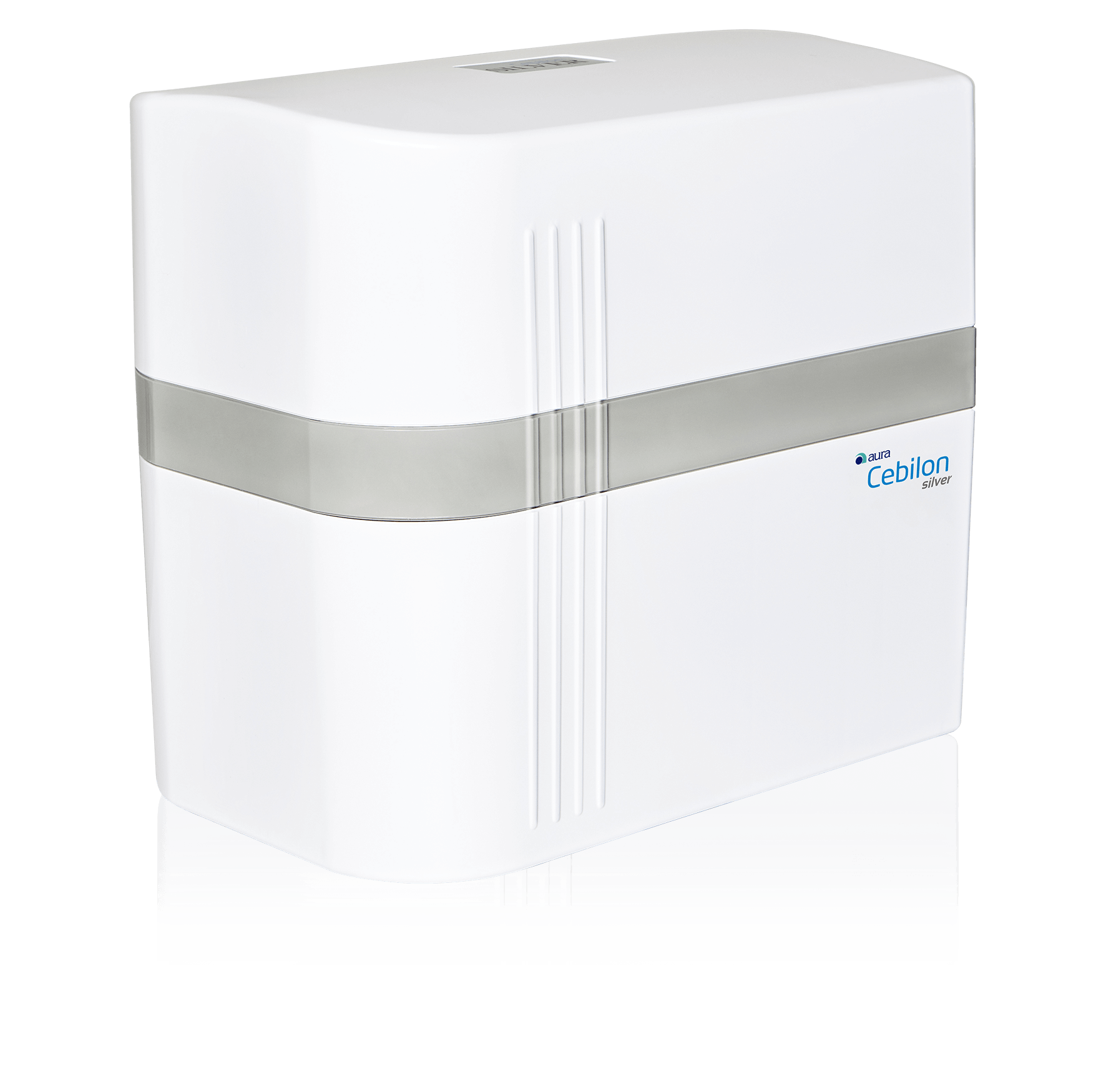
İhlas Aura Cebilon Platinum Uyumlu 5'li Filtre Seti Fiyatları, Özellikleri ve Yorumları | En Ucuzu Akakçe

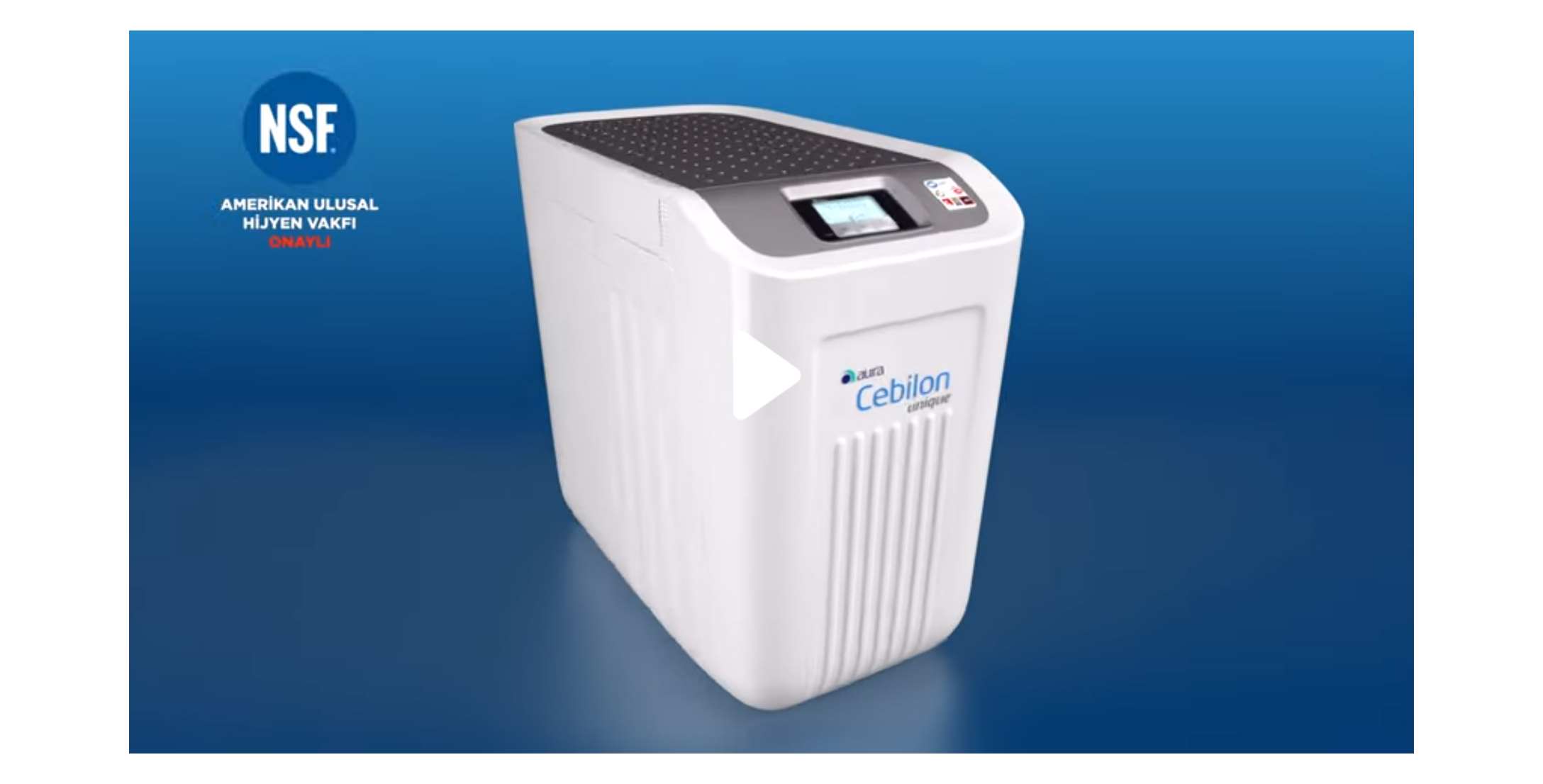
İhlas Pazarlama - Çok özel fırsat! World Kart ile Aura Cebilon Platinum Su Arıtma Cihazı şimdi aylık sadece 99 TL taksitle. Sağlıklı suyu evinizde kendiniz üretin. Ücretsiz tanıtım için başvurun. 444 49 49. | Facebook
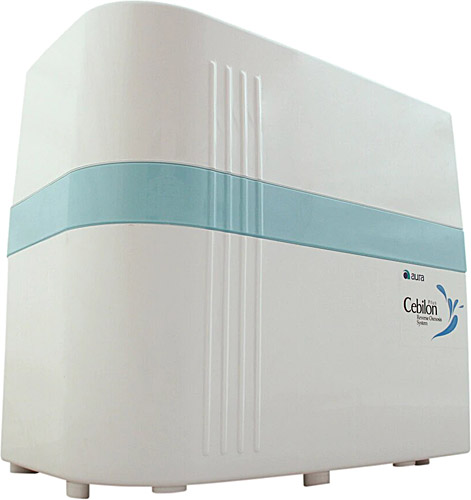

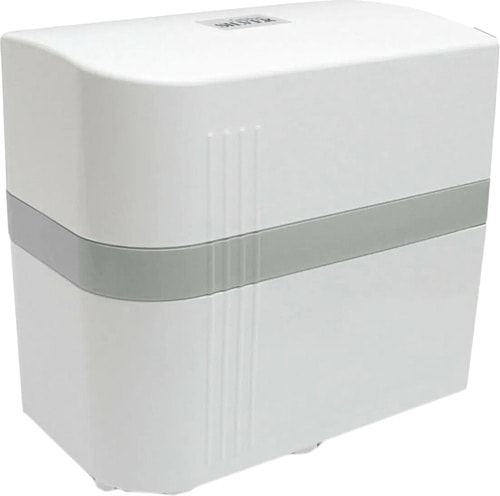
İhlas Aura Cebilion Plus 101 MF Su Arıtma Cihazı Fiyatları, Özellikleri ve Yorumları | En Ucuzu Akakçe