Egebey Çorap - A Kalite Toptan Çorap, Bayrampasa nerede, Otobüs, Metro veya Minibüs / Dolmuş ile nasıl gidilir?
Marti Çorap, çorap ve külotlu çorap mağazaları, Rüstem Paşa Mh., Sultanhamam Meydanı, No: 1/6, Eminönü, Fatih, İstanbul - Yandex Haritalar

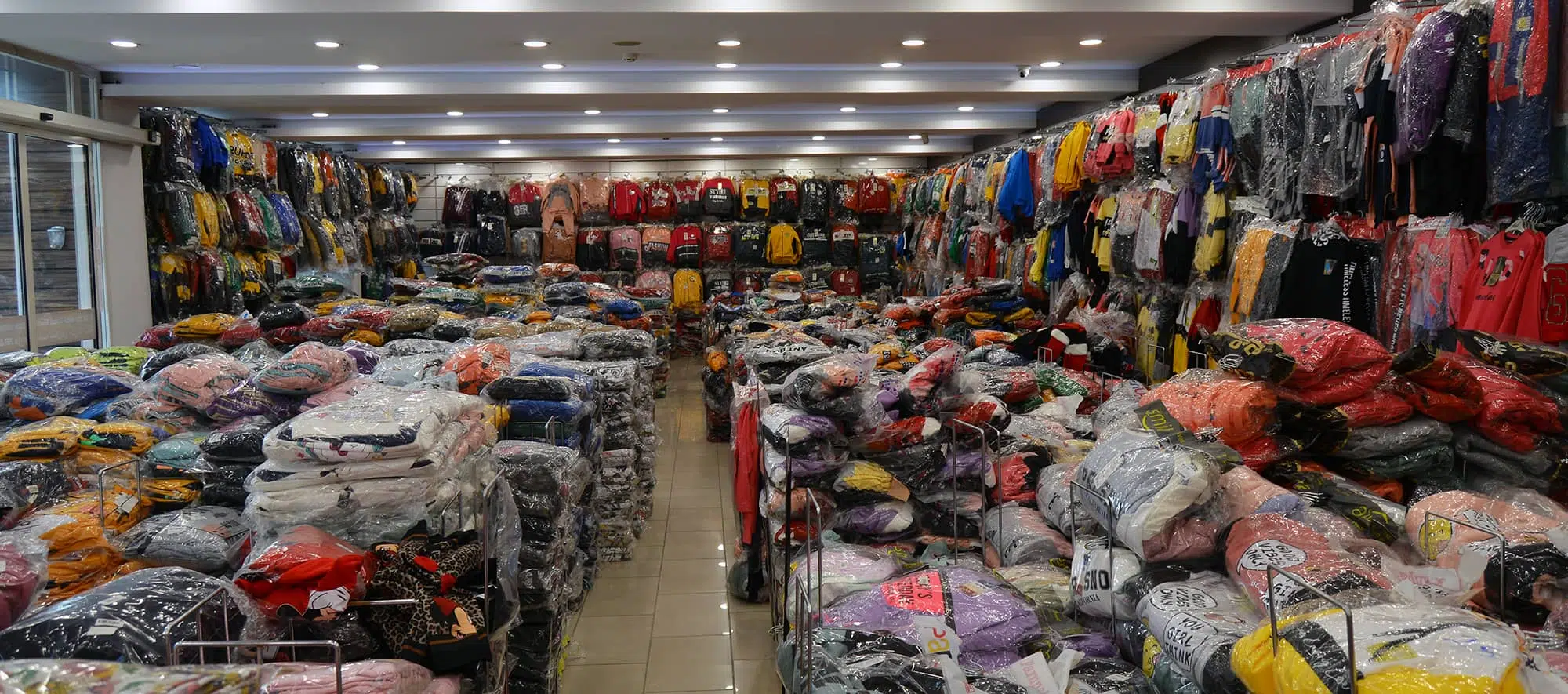
Toptan Çocuk Çorap - Toptan Bebek Çorap - Toptan Yenidoğan Çorap - Toptan Çocuk Çamaşır | Arti Magaza

Toptan Çorap | Çorap satışımız vardır toptan iletişim 05362014856 magzamız eminönü yeşildirek diri han 909 no | Facebook
İslamoğlu Çorap, çorap ve külotlu çorap mağazaları, Hobyar Mah., Hoca Hanı Sok., No:24, Fatih, İstanbul, Türkiye - Yandex Haritalar

🌞 İnternetten Çorap Aldık 🌍ÇorapToptancısı.com 👪Kargo Paketi Açılışı⭐️ Çorap Toptancısı Yorumlar - YouTube




















